🌲 Let’s Start Simple: What Exactly Is Hardboard (HDF)?
If you’ve ever admired the sleek finish of a painted cabinet or the sturdy base of laminate flooring, chances are, you’ve already met Hardboard, also known as High-Density Fiberboard (HDF).
Take it like this HDF is the stronger, tougher sibling of (Medium-Density Fiberboard) MDF. It’s produced by tearing wood fibers into small bits, adding resins and pressing them under extremely high heat and pressure. The result?
A dense, smooth, and incredibly strong sheet of engineered wood that looks great, works well, and lasts long.
While it may not get the spotlight like oak or maple, HDF quietly powers modern furniture, wall panels, and flooring systems around the world.
🧱 How HDF Is Made — The Science Behind Its Strength
The making of HDF starts with wood fibers — often from recycled or residual wood from sawmills. These fine fibers are combined with synthetic resins or binders, then subjected to massive pressure (over 800–1,000 kg/m³) and high temperatures.
This process bonds every fiber tightly together, removing air pockets and creating a uniform, ultra-dense material.
Unlike plywood (which uses layers of veneer) or MDF (which has a lower density), HDF feels heavier, stronger, and smoother.
👉 Fun fact: Because of its density, HDF boards are sometimes called “hardboard” — a term you might spot on flooring packaging or wall panel labels.
💪 Key Features of HDF That Make It Stand Out
So, what is it about HDF that has everyone from builders to designers to homeowners installing them? Let’s break it down:
1. Exceptional Density and Strength
HDF typically measures between 800 to 1,040 kg/m³, making it far denser and tougher than MDF.
What this means is that it’s unlikely to warp, split or crack easily when subjected to pressure — great for furniture or flooring on which needs to bear weight.
2. Smooth, Fine Surface
HDF is comprised of finely ground wood fibers giving it a very smooth finish without visible grain or knots.
Painters and laminators love it — paints, veneers or laminates will stick uniformly, giving that shiny, factory-finished appearance.
3. High Stability
Temperature swings and humidity can wreak havoc on natural wood — but not so much on HDF.
Its tight fiber structure makes it impervious to shrinkage less prone to seasonal movement.
4. Moisture and Warp Resistance
Not quite waterproof, but more resistant than MDF. When installed correctly (particularly around the edges), it can handle daily humidity very well — so kitchens, hallways or climate-controlled interiors are good examples.
5. Superior Screw and Fastener Holding
A frequent concern with MDF is the screws can work loose over time. HDF, which is denser material allows the screw and fasteners to anchor more efficiently meaning your furniture will last longer.
6. Eco-Friendly Option
Most HDF boards are made from recycled wood fibers — meaning less raw timber is cut.
That makes it a sustainable choice for environmentally conscious builders and consumers.
🛠️ Common Uses of Hardboard (HDF)
You might be surprised how often HDF shows up in everyday life. Here are some of its most common and creative uses:.
1. Furniture Manufacturing
Wardrobes, dressers, desks and even cabinet doors are just a few of the many popular uses for HDF in furniture manufacturing.
It provides a smooth base for laminates and paint, resists dents better than MDF, and offers lasting durability without the high cost of solid wood.
2. Flooring Substrate
HDF serves as the core layer in many laminate flooring systems. It’s a dense material that keeps the flooring panels flat and is resistant to wear from foot traffic.
And if you’ve walked on a laminate floor that is quiet and sturdy underfoot — you’ve probably walked on HDF.
3. Wall Paneling and Wainscoting
HDF panels provide a smooth, contemporary finish for commercial interiors, offices and homes.
They can be digitally printed, veneered or painted to look like anything from reclaimed barn wood to marble.
4. Mouldings and Decorative Trims
Easy to machine and great with holding shape, HDF is ideal for mouldings, skirting boards and other decorative profiles.
5. Doors and Cabinet Fronts
Many flush doors and kitchen cabinets use HDF as their core material — offering strength, smoothness, and a premium feel.
6. Acoustic Panels
HDF, being heavy and dense, it is used in sound absorptive panels for studios or theaters to help create an acoustic environment.
⚖️ HDF vs MDF — What’s the Difference?
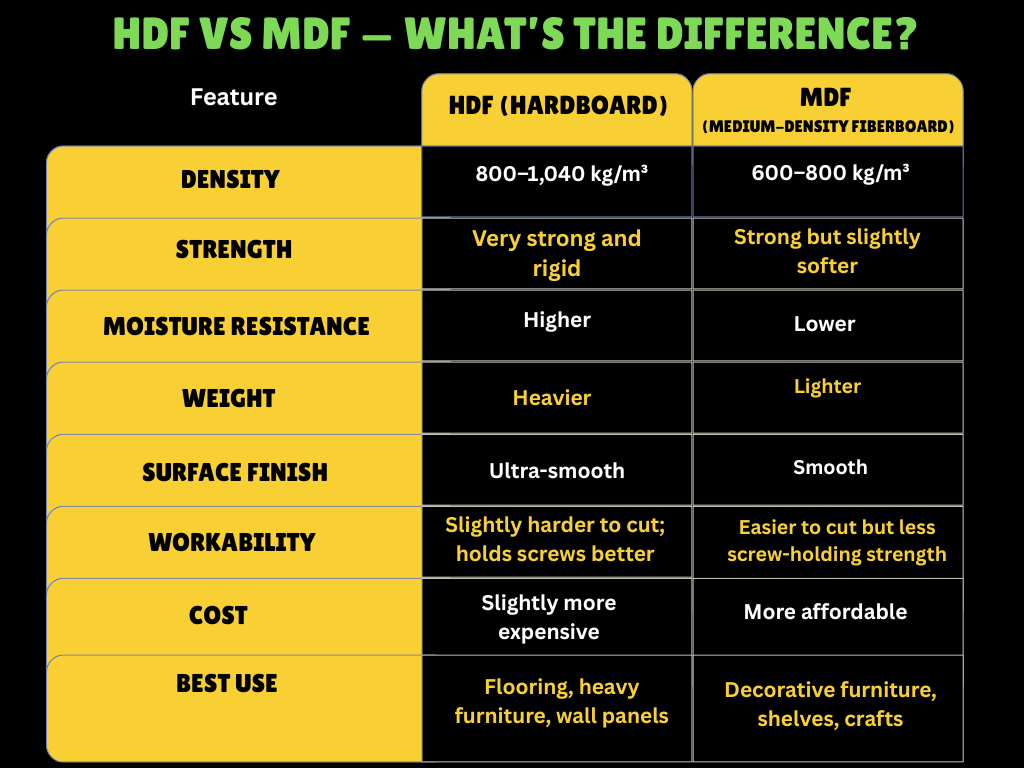
👉 Quick takeaway:
If you need something lightweight and easy to work with — go MDF.
If you need strength, durability, and a flawless finish — go HDF.
🌧️ How Does HDF Handle Moisture and Weather?
While HDF has better moisture resistance than MDF, it’s still not designed for outdoor or wet environments.
To make it last, you should always:
- Seal the edges and surfaces before painting or laminating.
- Avoid direct water exposure — use it in interiors only.
- Use treated HDF for slightly humid spaces like bathrooms or basements (these come with moisture-resistant additives).
Manufacturers also suggest HDF for indoor wall applications — but recommend FRP (fiberglass reinforced panels) for high-moisture zones like commercial kitchens or restrooms.
🧩 HDF vs Plywood — Another Common Comparison
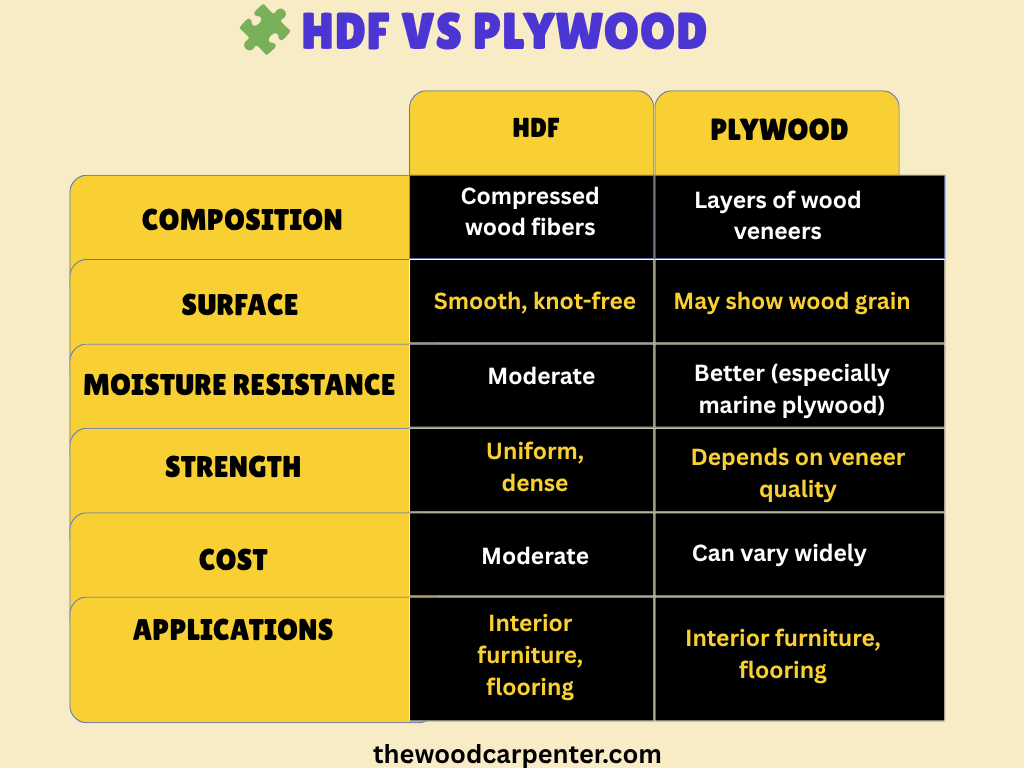
In short: plywood wins for outdoor use, but for indoor design and finish quality, HDF often outperforms.
🧰 Working With HDF: Tips From the Workshop
And if you’re getting ready to cut, drill or machine HDF here are a few handy tips:
- Use sharp carbide tools — dull blades may burn the edges.
- Pre-drill holes for screws to prevent cracking.
- Seal cut edges to prevent moisture absorption.
- Wear a mask — cutting HDF produces fine dust.
- Prime before painting for a smooth texture, added protection, more durable finish.
When treated right, HDF delivers excellent longevity and finish quality — perfect for both professionals and DIY enthusiasts.
🌎 Sustainability and Environmental Impact
One of the little-known strengths for HDF is that it’s eco-friendly.
Manufacturers often use wood residues, sawdust, and chips that might otherwise go to waste.
Plus, the dense structure means less raw wood is needed for the same strength you’d get from solid timber.
Some even make low-formaldehyde or no-added-formaldehyde HDF boards that meet the stringent U.S. indoor air quality standards — good news for sustainable builders and homeowners alike.
💰 Cost and Value
HDF is slightly more expensive than MDF but cheaper than solid wood or premium plywood.
But what you sacrifice in cost is added back in durability, better finishing and maintenance.
Whether for floor coverings, wall panelling or heavy-duty furniture – HDF gives a impressive return on investment.
💡 Final Thoughts: Why HDF Deserves More Attention
Hardboard (HDF) isn’t as glamorous, but it’s a workhorse material, quietly supporting a multitude of interior projects with its strength, precision and versatility. Whether you’re outfitting a room with durable flooring, crafting fine furniture or simply adding detail to home decor—HDF is an elegant and economical material.
It bridges the gap between good price and good quality; by offering the perfect balance for homes, commercial spaces.
❓ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Is HDF waterproof?
Not completely. It’s somewhat moisture-resistant, but should not come in contact with standing water. Always seal the edges and surfaces for better protection.
2. Is HDF better than MDF?
In terms of strength, density, and screw-holding capacity — yes, HDF performs better. But MDF is easier to cut and more budget-friendly for lighter applications.
3. Can HDF be used outdoors?
No. HDF is designed for indoor use only. For outdoor projects, go for marine plywood or exterior-grade fiberboard.
4. Can you paint or laminate HDF?
Absolutely! Its smooth surface takes paint, veneer, and laminate beautifully — one reason it’s so popular in furniture and flooring industries.
5. Is HDF eco-friendly?
Yes. Many HDF products are manufactured from recycled wood fibers and low-emission resins, making HDF a genuine environmentally friendly product.

