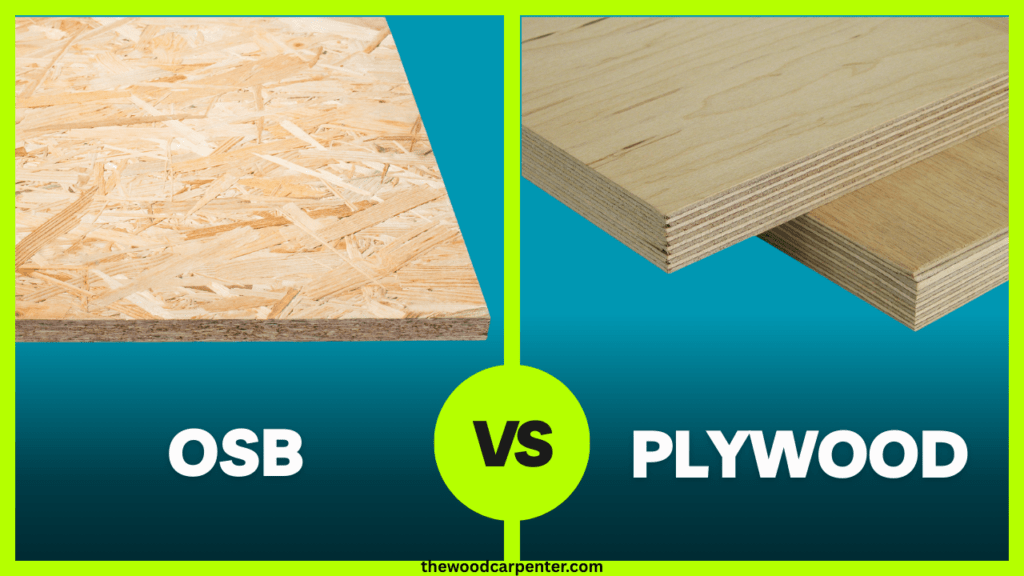
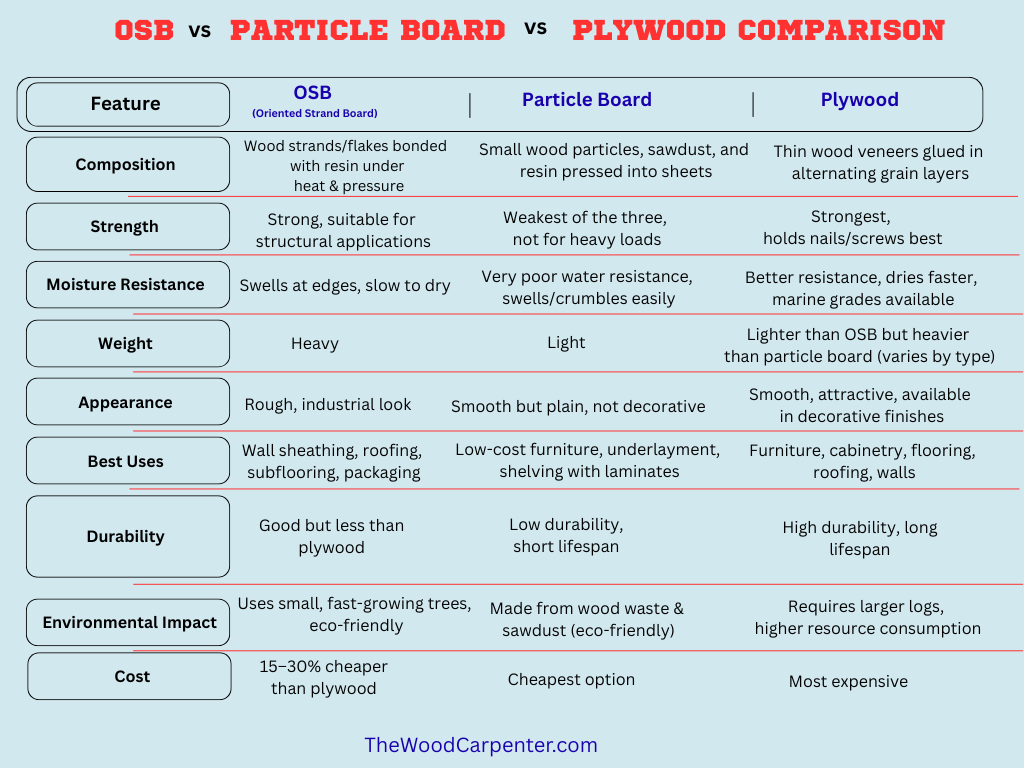
When it comes to framing, sheathing or constructing furniture, two engineered wood products will mostly dominate the conversation which is OSB (Oriented Strand Board) and Plywood. Although both are popular materials for construction and wood-working, but they vary in strength, resistance to moisture, cost, look and performance. If you are debating which to use OSB or Plywood for your project, then learn the facts that can help you decide here.
What is OSB?
OSB (“Oriented Strand Board”) is a engineered panel made from wood strands or flakes that are oriented and bonded together in layers with the long direction of the strands aligned with the panel axis. The result is a cohesive sheet with less large voids. OSB is commonly used for:
- Roof decking
- Wall sheathing
- Subflooring
- Industrial packaging and crates
Because OSB takes smaller, faster-growing trees to produce, it’s also thought that it’s more eco-efficient than plywood.
What is Plywood?
Plywood is produced by peeling thin veneers from logs and gluing them together with alternating grain directions under heat and pressure. Plywood’s sheets are bonded with one another using a cross-lamination process, and lends plywood high dimensional stability. It is commonly used for:
- Furniture and cabinetry
- Flooring and underlayment
- Roofing and walls
- Decorative panels and visible finishes
Plywood comes in a variety of grades; softwood plywood for construction and hardwood for furniture along with special type like marine plywood which is water proof, makes it uniquely flexible due to its numerous potential uses.
Pros and Cons of OSB
Pros
- It is more affordable than plywood
- Even panels with little or no soft spots & voids
- It is Environmentally friendly because it uses small, fast-growing trees
- Large panel sizes available for construction
Cons
- Heavier than plywood
- Swells and holds water longer, which may cause decay
- Do not hold nails and screws as firmly
- Rough appearance, makes them unsuitable for decorative work
Pros and Cons of Plywood
Pros
- It is stronger and stiffer than OSB
- It can hold nails and screws securely
- Resists swelling and warping better
- Because of it’s smooth surface it is suitable for visible and decorative use
- They are available in many grades (softwood, hardwood, marine, fire-retardant)
Cons
- More expensive than OSB
- It is prone to delamination if it is exposed to prolonged moisture
- May contain knots or voids in the lower grades
Also read:
CDX vs OSB: Which One Is the Best for Your Next Project?
Which One Should You Choose ?
For your decision of OSB or plywood, it all comes down to where and how you will be using them:
For structural applications (roofing, wall sheathing, subflooring): OSB is affordable and strong as long edges are sealed and moisture exposure is limited.
For furniture, cabinetry, or visible projects: Plywood gets the nod here thanks to its smooth surface and better appearance.
For humid or damp environments: Plywood is superior as it doesn’t expand as much and reverts closer to its original size once it has dried.
For budget projects: OSB is 15-30% cheaper than plywood — If you are aiming for a little extra savings, OSB is the cutter where cost considerations are crucial.
OSB vs Plywood in Construction
Roofs: OSB is common because it’s less expensive, but plywood works better over the long run in a damp climate where mold and moisture are more likely.
Walls: Both are fine. Other than the final appearance of your wall, OSB gives you large uniform sheets, making installation a snap.
Floors: For floors under tile or hardwood, I would choose plywood because it is much stiffer and will not bounce or squeak.
OSB vs Plywood Strength
They are both strong for structural use, but plywood tends to be stiffer and holds nails/screws a bit better while OSB has similar strength everywhere but can flex slightly when loaded.
OSB vs Plywood for Walls
OSB is popular for wall sheathing because it’s cheap, uniform and comes in large panels. Plywood also works well, which is a bit stronger, especially if you live in a humid area.
OSB vs Plywood for Roofing
OSB is inexpensive, which is why it’s commonly used for roof decking, but plywood has greater moisture resistance and a quicker drying time that makes it the safer option for rainy or humid areas.
OSB vs Plywood Flooring
For both subfloors and finished floors, plywood is the stiffer material that holds fasteners better and has less bounce or squeaks. OSB is still found in the majority of subfloors, but it can swell at the edges if it comes into contact with water.
OSB vs Plywood for Shelving
When it comes to shelving and furniture, think plywood with its smooth surfaces, screw-holding capabilities, and nice appearance. Plywood is the winner. The OSB finish is very rough and not at all appealing to the eye.
OSB vs Plywood Water Resistance
Plywood performs better in wet or humid conditions, as it swells less and dries faster.
Plywood works better in wet or damp settings, because it doesn’t swell as much and dries quicker. OSB absorbs more water, swells at the edges, and takes much time to return to it’s shape.
FAQs on OSB vs Plywood
1. Is OSB stronger than Plywood?
OSB is strong and it is suitable for structural applications, but plywood is generally stiffer and it holds the fasteners better.
2. Can OSB be used outdoors?
Yes, but only if edges are sealed and it is not exposed to prolonged moisture. Plywood, especially exterior or marine grade, performs better outdoors.
3. Which is cheaper: OSB or Plywood?
OSB is typically 15–30% less expensive than plywood of similar thickness, making it a more budget-friendly option.
4. Does OSB or Plywood last longer?
Plywood will typically lasts longer, especially in the humid or wet conditions, because it resists swelling and dries faster.
5. Which is better for furniture?
Plywood is better for furniture and cabinetry due to its smooth finish, appearance, and ability to hold screws securely.
Final Thoughts
When comparing OSB vs Plywood, there is no one-size-fits-all answer.
If budget and structural performance are your focus, then choose OSB. But if appearance, wet strength, and long-term stability matter more to you than cost, buy Plywood.
By learning about the unique benefits and advantages of each, you can decide which one is best for your project, guaranteeing that structurally sound, low-maintenance and economic choice you need.

