Wood Putty vs Wood Filler: Which One Should You Use?
When fixing wood, very often the question for homeowners and DIYers is not “Am I going to use a wood putty or wood filler?” At a superficial level, these two products are very similar looking and feeling. Both are paste-like substances meant to fill in wood imperfections. “But they have different purposes. Choosing the right one can make the difference between a seamless repair and a patch that stands out for all the wrong reasons.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explain everything you need to know about wood putty vs. wood filler—how they’re are made, when you should use them, and the pros and cons of each — including their outdoor performance and expert tips. In the end, you’ll have a clear idea of which is best suited to your next project.
What Is Wood Filler ?
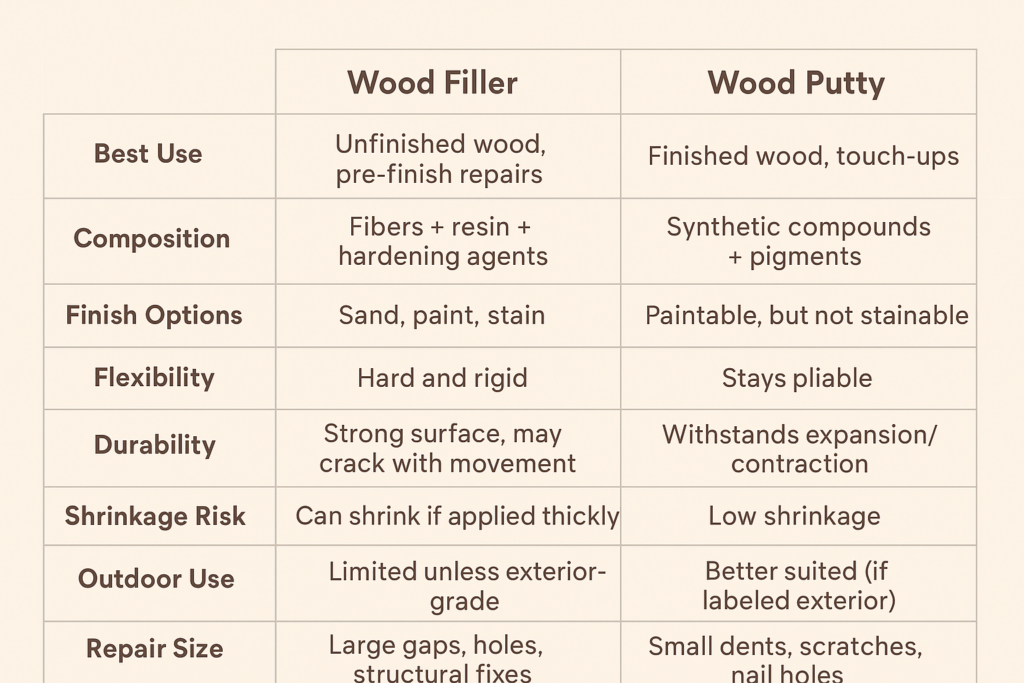
Wood filler is a compound made from wood fibers, resin, and a hardening agent. Once applied, it cures into a rigid, solid surface that can be sanded, painted, or stained. Filler frequently accepts stain better than putty since it actually has wood fibers in it, allowing the filler to take the color more naturally to the unfinished wood.
Wood filler is best used before applying any finish. That could be raw furniture, new floors, its trim work, cabinetry or any wood project that still has yet to be sealed, varnished or painted.
Key Features of Wood Filler
- Hardens after curing
- Sandable and stainable
- Perfect for filling gaps, holes and gouges
- Best for unfinished wood
- May shrink or crack if not applied properly
What Is Wood Putty ?
Wood putty, sometimes called plastic wood, is a pliable material made from synthetic resins, oils, and pigments. It doesn’t dry completely, unlike wood filler. Rather, it exhibits some flexibility after curing which allows the sealant to stretch and compress while in use, such as surfaces that are prone to expand/contract due to humidity or temperature changes.
Wood putty is for finished wood surfaces: furniture, floors and trim that already have stain, varnish or paint. Because it doesn’t take stain well, it typically comes in a variety of colors that can be color-matched to the existing finish.
Key Features of Wood Putty
- Remains flexible after curing
- Comes pre-stained in several wood colors
- Not sandable or stainable
- Best for finished wood
- Covers minor nicks, scuffs, and small holes
Wood Putty vs Wood Filler: Side-by-Side Comparison
Also read:
Oil-Based Stains: A Guide for Long-Lasting Wood Finishes
Butcher Block Oil: A Complete Guide for Lasting Wood Care
When to Use Wood Putty
You should use wood putty if:
- The surface has already been finished (stained, sealed, or painted).
- You are fixing up some small dings, scratches or gaps.
- You need a product that remains flexible with wood movement.
- You want a quick fix without re-finishing the whole surface.
Example: Your dining table gets a small scratch after years of use. A color-matched putty stick can fill it in so it disappears without stripping or re-staining the entire tabletop.
Pros and Cons of Wood Filler
Pros
- Hardens to a durable, sandable surface
- Can be stained or painted to match raw wood
- Excellent for unfinished carpentry projects
- Quick-drying formulas available
Cons
- Not suitable for finished surfaces.
- May crack or shrink over time.
- Poor outdoor durability unless formulated for exterior use.
- Needs sanding and finishing afterward.
Pros and Cons of Wood Putty
Pros
- Flexible, resists cracking from wood movement
- Great for already finished surfaces
- Available in a wide variety of colors
- Simple application—no sanding required in many cases
Cons
- Not stainable (color options must be matched)
- Can damage raw, unfinished wood
- Longer curing time than filler
- Less rigid, not for large repairs
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Applying wood filler to finished wood – It will not bond well, and will stand out against the finish.
- Attempting to stain wood putty — Putty doesn’t take stain, so the repair will appear in a different color.
- Filling huge gaps with putty — Putty is for tiny flaws, not structural repairs.
- Not sanding the filler – Wood filler needs to be sanded level prior to finishing.
- Using indoor filler for outdoor spaces — Always read labels for weather-resistant or exterior-grade versions.
Outdoor Applications: Which Works Better?
If your project is outdoors — say, if you’re replacing deck boards, siding or exterior trim — then extra precautions need to be taken.
Wood filler: The typical versions are not water-resistant. But some exterior-grade fillers can be used outdoors. These can be effective if the objects are painted or sealed afterward.
Wood putty: More flexible, and thus more likely to hold up better outdoors, particularly in areas with large humidity or temperature variations.
If in doubt, go for the product listed as exterior grade and always seal with something protective.
Pro Tips for Best Results
Match colors carefully: Use the closest pre-tinted color, with putty. For the filler apply test stains on scrap wood and check that color matches.
Overfill slightly: Filler has a tendency to shrink, and putting on too much here will give you a flush surface after sanding.
Use wood dust: For a invisible repair, mix fine sawdust from your project with filler to match exactly the color and grain.
Seal repairs: Never forget to finish with paint, varnish or sealant in line with longevity.
Check compatibility: While most fillers and putties adhere to all finishes, some may not stick to certain woods or finishes; you should always test them first.
Which One Should You Choose?
It is really all about one simple thing: The wood is finished or the wood is unfinished?
Unfinished wood → Use wood filler.
Finished wood → Use wood putty.
For outdoor projects, make sure the product is rated for exterior use, and always seal afterward for protection.
Final Thoughts
The use of both wood putty and wood filler is necessary for most woodworkers, do-it-yourselfers and even homeowners. But they’re not interchangeable. When you use them right, your repairs will be more seamless, last longer and keep your wood looking pretty.
Consider wood filler your best pal for taking on unfinished jobs and bigger repairs, while wood putty is like a private tool for finished products and small fixes. With the proper selection, your woodworking projects will be neat as well calculating.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is wood filler the same as wood putty?
No. Wood filler is designed for unfinished wood and hardens after curing, while wood putty is for finished wood and stays slightly flexible.
2. Can wood filler be used on finished wood?
No, Wood filler does not adhere well to finished surfaces. It’s intended to be used before staining, painting or sealing.
3. Can wood putty be sanded or stained?
Wood putty cannot be sanded or stained. It comes pre-colored to match finishes and is usually paintable.
4. Which is stronger, wood filler or wood putty?
Wood filler is more resistant and produces a tough, solid surface. Putty is a bit more flexible, but it’s not as firm or rigid, so it works better for very small touch-ups.
5. Can I use wood filler outdoors?
Yes, but only if it’s labeled exterior-grade and has been sealed the right way. Traditional wood filler is not water resistant.
6. Is wood putty waterproof?
The majority of those wood putties are water-resistant, but not completely waterproof. Never use anything that isn’t rated for outdoor use.
7. What’s better for nail holes—wood filler or wood putty?
For nail holes in unfinished wood, use wood filler; for those in finished wood, opt for wood putty.
8. Does wood filler shrink?
Yes, wood filler can shrink or crack as it dries, particularly when used in large gaps. Always overfill slightly and sand smooth.
9. Can you paint over wood putty?
Yes. Most wood putties are paintable, although you can’t get them to soak up a stain. Pick a color that is closest to your finish for optimal success.

